555 Timer Driving LED
For a monostable circuit, we join the threshold and discharge pins for the timing circuit, and apply the trigger pulse through pin 2. Therefore, this circuit will light the LED after a delay.
- Section A is responsible for the proper triggering of the circuit. It consists of a 4.7 kΩ pull-up resistor, and a push to make switch. Pressing the switch generates a negative going spike into pin 2 forming the basis of a trigger.
- In section B we see pins 6 and 7 joined, and there is a resistor and capacitor also joining to that common point forming the basis of the timing circuit. It is usually a monostable circuit when pins join in this way. The value of the capacitor and resistor determine the time delay.
- Section C is the 555 timer IC.
- Section D is responsible for the output. When the output is high, the voltage there is close to Vcc, which is 9 V. A high output would therefore light the LED. The 680 Ω resistor provides a voltage drop for the LED.
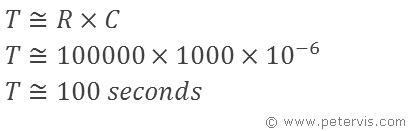
To calculate an approximate value of the time delay we use the following formula and calculation.
Related Articles
555 Timer Driving LED555 Astable Flashing LED
555 Timer Dual LED Flasher
555 Astable with Dual Flashing LEDs
