ICL7106 / ICL7107 Integrate Values
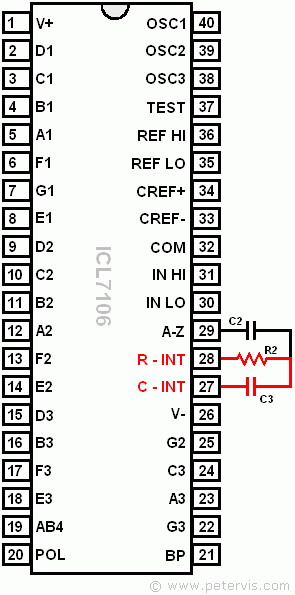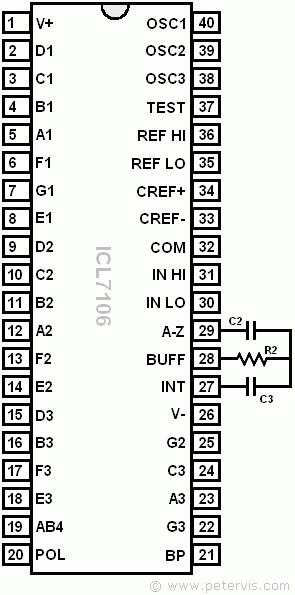
The integrate capacitor CINT connects to pin 27, and the integrate resistor RINT connects to pin 28. These components are marked C3 and R2 respectively on the documentation circuit, and their purpose is to determine the full-scale reading. There are two options for the full-scale reading, and my design shall be utilising the 2 V option.
Calculate R2

We require a full-scale swing of 2 V therefore VINFS is set to 2. The documentation suggests that the optimum value of IINT is 4 µA. This value comes from the integrators ability to supply 4 µA of drive current and still remain within the linear region of its characteristics. As you can see from the calculation above, by using the optimum recommended values for a 2 V full scale reading, R2 is calculated to be 500 kΩ. Therefore, a 470-kΩ resistor is the nearest standard value that should work.
Calculate tINT
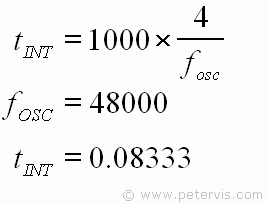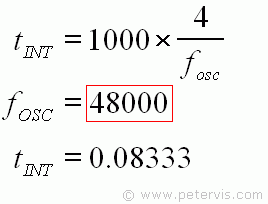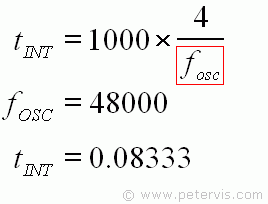
Before the value of CINT is calculated, the integration period tINT is first required, using the formula given. Since the typical oscillator frequency is 48000 Hz, tINT is 0.08333.
Calculate C3
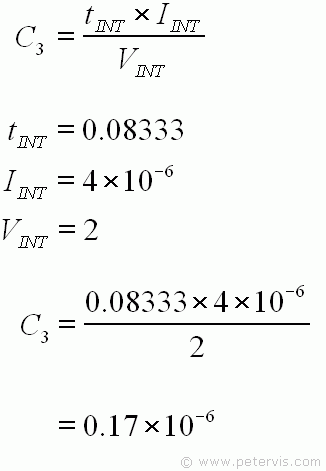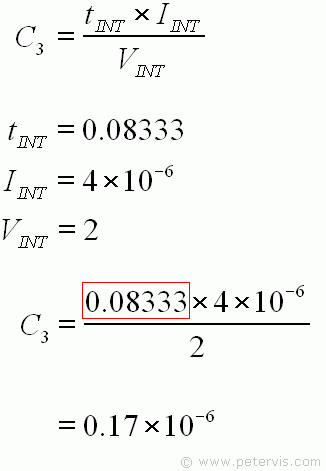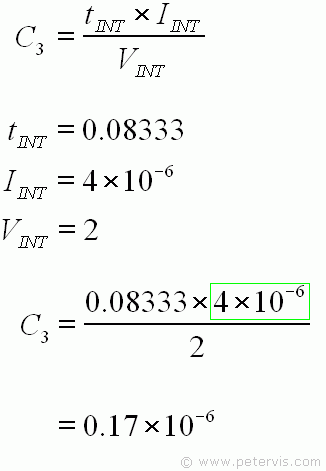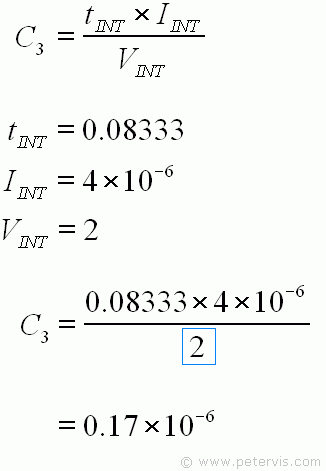
We have all the values needed to substitute into this formula. The value of tINT was calculated earlier, IINT is the optimum value given for the reasons stated earlier in this page, and VINT is the full reading of 2 V for this circuit. Therefore, the calculation gives 0.17 µF for the value of the integrate capacitor C3.
According to the documentation, when the clock frequency is 48 kHz, there will be three readings per second taken, and the best nominal value for CINT is 0.22 µF. When the analogue common provides a reference, a 2 V full-scale reading is fine for this value.
This Article Continues...
ICL7106 / ICL7107 Digital Meter DesignICL7106 / ICL7107 Oscillator Frequency
ICL7106 / ICL7107 Integrate Values
ICL7106 / ICL7107 Pin Settings - Part 1
ICL7107 LED Display Settings
ICL7660 Voltage Converter
ICL7106 and ICL7107 Digital Meter Circuit