Class AB Amplifier
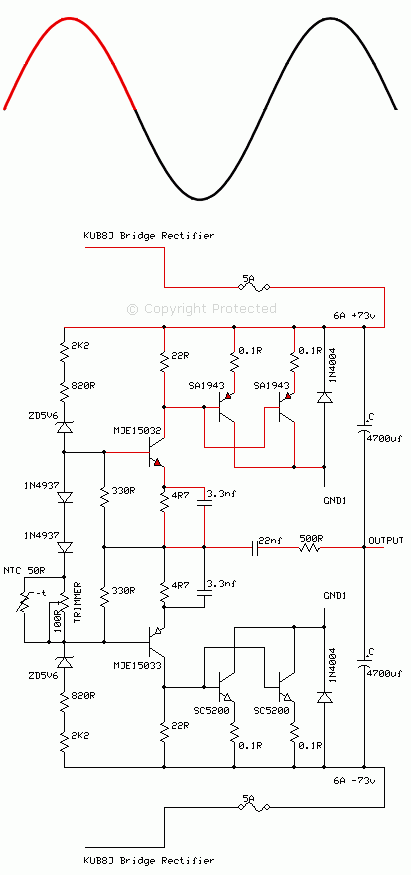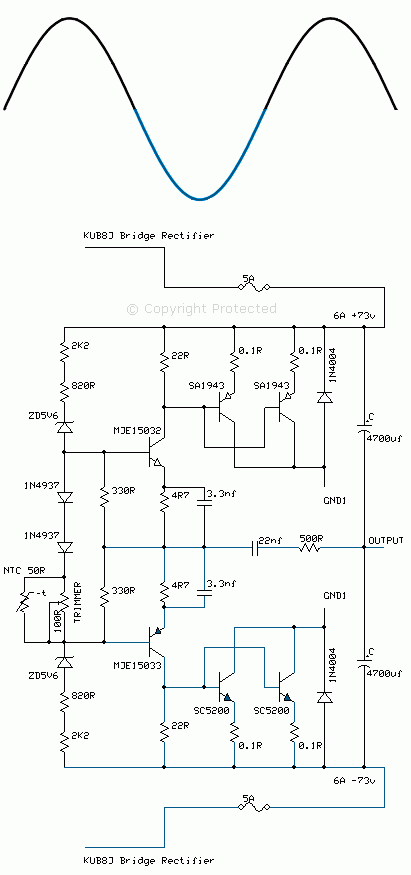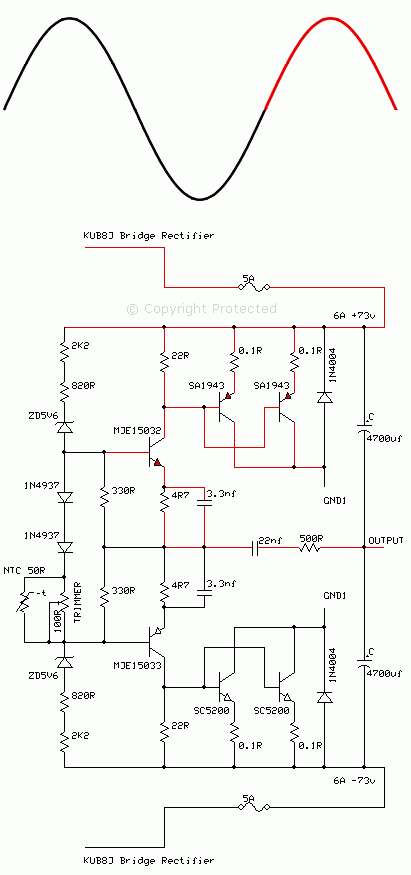
In a Class AB complementary symmetrical output stage, a complementary pair of transistors conduct separately for the positive half of the cycle and the negative half. The matched sets of transistors connect in an emitter follower mode and drive the speaker directly. This type of design is fairly efficient and cost-effective.
The circuit shown above is the output stage of an Alto PBM8 500 MK2 powered mixer amp. The circuit operates over split-voltage rails of 73 V, with a 5-amp time delay fuse. In this design, the power transistors connect in parallel to increase the power handling capability of the bipolar junction transistor (BJT), hence a pair of SA1943 transistors connect together receiving the same signal to their base junctions. This arrangement mirrors the opposite half of the phase, with a pair of SC5200 transistors connected in parallel.
Drivers
The drivers to the final output stage are the MJE15032 and MJE15033 complementary pairs.
Q-Point
In a class AB arrangement, the operating point "Q" has to lie within the cut-off region for ideal operation. In practice, a small portion of the positive cycle and negative cycle remains forward biased near the cut-off region, therefore to minimize this error a trimmer brings the Q point closer to the cut-off region. As the transistors heat up, the Q point will drift, hence the NTC temperature sensor is used to compensate for this thermal drift.
This Article Continues...
PBM8 500 MKIIPBM8 500 MKII Inside Look
PBM8 500 MKII Diagnostic Logic
PBM8 500 MKII Fault Solved!
Power Resistor
Amplifier Heat Sink
Class AB Amplifier
How to Check Transistors
GCA5200T and GCA1943T Transistors
2SC5200 2SA1943 Transistor Replacement
PBM8 500 MKII Diagnostic LEDs
PBM8 500 MKII Power Supply