AVO 8 MK 2 Moving Coil Meter

An advantage, which AVO 8 Mk 2 has over AVO 7 Mk 2, is that it has a much more sensitive meter movement. On DC ranges, the Mk 2 meter movement has a sensitivity of 2000 ohms per volt, which means that as little as 50 µA through the voice coil can cause full-scale deflection of the needle.

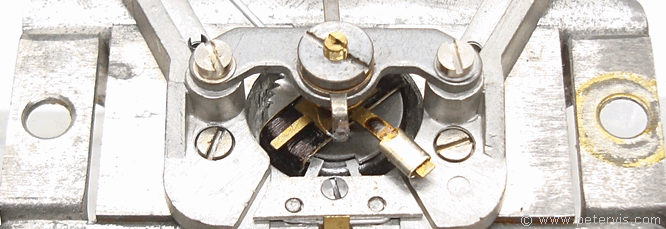
The AVO 8 moving coil meter is an extremely high quality electromechanical component based on the Weston movement, which uses a magnetic field to cause the needle to deflect. A uniform gap between two permanent magnets focuses the magnetic field into the channel and enables the meter to produce a linear response. Thus, the needle deflection is proportional to the current through the coil. Consequently, the 5-inch scale has uniformly divided graduations.
This meter movement uses an aluminium former wound with copper wire supplemented with constantan. Since aluminium is light, it makes the movement very sensitive to small currents. The constantan minimizes errors caused by thermal variations.


The red magnets are a pair of "Alcomax" blocks forming a uniform air gap. The springs are made of phosphor bronze, which carry the current as well as provide the restoring torque. There are two springs, which produce almost equal and opposing forces, which is why the needle exhibits a damped response.
A moving coil meter provides an averaging display; hence, if one were to pass an AC current through it, then the needle will remain steady around the zero mark. Therefore, to measure AC currents a rectifier is typically used.
Movement Reverse Control
Coil meters are sensitive to the direction in which the current flows through the coil, as it determines the direction of the deflection. As a result, the MK 2 meter has a push-button switch "Movement Reverse Control" to reverse the polarity. The button is marked "REV. M.C." on the front panel.
Calibration

The meter must be oriented horizontally when calibrating the moving coil meter. Just above the AVO logo, there is a screw used to calibrate the needle to zero position.
There are also three small knobs marked "ZERO Ω", "ZERO Ω / 100", and "ZERO Ω × 100". These calibrate the three resistance ranges. Calibration is necessary as the battery charge influences the readings; hence, you must perform this calibration before taking any resistance measurements. The test leads connect together and the selector switch set to the desired range, then one adjusts the relevant knob for a zero reading of the pointer.
Damped Meter Response

A damped meter movement is often a sign of a thoughtfully designed high quality meter. To produce a damping force, they use an aluminium former for the voice coil, which helps to produce electrical damping. When the coil rotates, the former cuts lines of flux and induces a voltage. This voltage, through the production of eddy currents, produces a magnetic field in opposition to the field of the permanent magnet. This opposing field has a breaking effect, which eventually slows the pointer down.
On cheap meters, the spring loaded needle shoots back to its resting position and even bounces! Hence, Avo Meters are a very nice example of good engineering. This Avometer movement is so sensitive that simply blowing air on the needle causes it to deflect. This is why a draught proof room is required for calibration purposes.
This Article Continues...
AVO 8 MK 2AvoMeter 8 Range
AVO 8 Battery Replacement BLR121 / B121
AvoMeter 8 MK2 Inside View - Animation
AVO 8 MK 2 Circuit Diagram / Schematic
AVO 8 Test Leads, Probes, and Terminals
AVO 8 Specification and Features
AVO 8 Repair Service / Problems
AVO 8 MK 2 Moving Coil Meter
AVO 8 Circuit and Components
AVO 8 History
AVO 8 Back Cover
AVO 8 MK 2 Meter Dial Accuracy